Understanding Physical Therapy's Role in Pain Management
Physical therapy has become a cornerstone in contemporary pain management strategies, offering a non-invasive, evidence-based approach to alleviate pain and improve function across a broad spectrum of conditions. With growing concerns about opioid dependency and surgical interventions, physical therapy's role is increasingly scrutinized through rigorous research to quantify its success and effectiveness. This article explores the success rates of physical therapy for pain relief, analyzing comprehensive research findings, patient satisfaction levels, and emerging trends that shape its evolving landscape.
Research-Backed Evidence on Physical Therapy Effectiveness for Pain Relief
What do research studies and scientific evidence say about the effectiveness of physical therapy for pain relief?
Research and scientific findings unequivocally support the use of physical therapy as a highly effective intervention for managing pain across many conditions. Numerous peer-reviewed studies published in reputable journals, including the Physical Therapy Journal (PTJ), consistently demonstrate that targeted physical therapy approaches—such as therapeutic exercises, manual techniques, and modality treatments—lead to significant pain reduction and improved function.
For instance, a comprehensive meta-analysis by Goethe University Frankfurt evaluated data from over 10,000 patients with chronic low back pain. The results showed that individualized treatment plans increased success rates in pain relief by 38%, and when combined with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), success rates soared by 84%. This highlights the importance of personalized, multimodal treatment strategies.
Numerous randomized controlled trials confirm that therapies utilizing modalities like ultrasound, TENS, hot packs, and therapeutic exercises effectively decrease pain levels. Patients often experience a 40-50% reduction in pain intensity after 4-6 weeks of therapy, alongside substantial improvements in functional capacities.
This body of research consistently underscores the value of physical therapy not only in acute pain management but also in long-term rehabilitation, reducing reliance on medications, surgery, and opioids. The scientific consensus and robust experimental data firmly establish physical therapy as a credible, evidence-based approach for pain relief and enhancing quality of life.
Statistical Success Rates of Physical Therapy Treatments

What do studies show about overall success rates of physical therapy?
Research indicates that the success rate for physical therapy interventions generally falls between 68% and 72%. This means most patients experience meaningful improvements in movement, pain levels, and overall function after completing therapy courses.
How much do patients typically experience improvements in pain and function?
Patients often report a 40-50% reduction in pain intensity within 4 to 6 weeks of beginning physical therapy. Additionally, about 70% of patients experience significant enhancements in their ability to perform daily activities and an improved quality of life.
How do success rates vary among different conditions?
Success rates are highest in conditions like acute lower back pain, post-surgical orthopedic rehabilitation, ankle sprains, and shoulder impingement, where 80-90% of patients report substantial improvements. Conversely, more complex or chronic conditions such as severe arthritis or neurological disorders tend to have success rates between 60-80%.
What does meta-analytical research reveal about individualized and multimodal treatments?
A comprehensive meta-analysis by Goethe University Frankfurt examined over 10,000 patients with chronic low back pain. It found that tailoring treatment to individual needs increased pain relief success rates by 38%. When combined with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), success rates surged by an additional 84%. This underscores the effectiveness of personalized, multimodal approaches in managing chronic pain.
In conclusion, the data consistently demonstrate that physical therapy is highly effective, with most patients experiencing significant pain relief and functional gains. The integration of individualized and cognitive interventions further enhances these outcomes, supporting the role of tailored, comprehensive rehabilitation in effective pain management.
Patient Satisfaction and Perceptions of Physical Therapy

What is the patient satisfaction rate for physical therapy?
Research indicates a high level of satisfaction among patients undergoing physical therapy. In a notable private practice setting in Australia, 86% of patients reported that they found physical therapy helpful. Moreover, 87% expressed a strong willingness to recommend their therapist’s services to others, highlighting the positive perceptions of care received.
Factors influencing satisfaction and recommendation rates
Patient satisfaction is significantly influenced by several factors, including the quality of communication and education provided by therapists. When therapists take the time to explain treatment plans clearly and involve patients in decision-making processes, satisfaction scores tend to increase. For example, providing effective advice that helps patients avoid future issues enhances their confidence in the treatment.
Additionally, therapists’ self-rated comfort levels in managing chronic pain significantly impact patient experiences. Higher comfort levels from therapists correlate with increased rates of patient self-discharge, indicating that patients are more likely to feel confident and supported during their care.
Role of education and communication in therapy outcomes
Effective communication and personalized education play crucial roles in improving overall therapy outcomes. Patients who receive tailored information about their conditions and treatment options tend to have better engagement and compliance, which leads to enhanced satisfaction and success rates.
Overall, high satisfaction rates are the result of attentive, personalized care that emphasizes education, clear communication, and active patient involvement. These aspects contribute to positive experiences, higher likelihood of recommendations, and better long-term outcomes.
Physical Therapy Versus Other Pain Relief Interventions: Outcome Comparisons
How do physical therapy outcomes and success rates compare with other pain relief interventions?
Research consistently shows that physical therapy provides outcomes comparable to, or better than, other pain relief options such as medication or surgery. Patients treated with physical therapy often experience significant reductions in pain — averaging a 40-50% decrease — and substantial functional improvements after just a few weeks. Success rates for physical therapy typically range between 68% and 72%, with many patients reporting high satisfaction levels (up to 98%) and improved quality of life.
Unlike pharmaceutical interventions, physical therapy emphasizes active participation through exercise and manual techniques, avoiding the risks associated with long-term medication use, such as opioid dependency. When combined with psychological approaches like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), individualized physical therapy achieves even higher success rates, up to 84% in pain relief.
Surgical options, while effective in certain cases, carry higher costs, longer recovery times, and increased risk of complications. Studies demonstrate that early physical therapy can reduce the likelihood of surgery by about 33%, making it a valuable first-line treatment in many musculoskeletal conditions.
Therapists who deliver higher levels of manual and active therapy tend to produce better clinical outcomes, particularly in patients with more severe baseline disabilities. This emphasizes the importance of targeted, consistent therapy.
Cost-effectiveness is another strength of physical therapy. It can reduce healthcare costs by up to 70% compared to invasive procedures and decrease reliance on opioids by 45%, contributing to safer, less costly patient care.
Overall, findings support physical therapy as a high-value treatment. It effectively improves mobility and reduces pain, providing a patient-centered approach that aligns well with clinical and economic goals in pain management.
Effectiveness of Physical Therapy in Managing Chronic Pain
How effective is physical therapy for managing chronic pain?
Physical therapy proves to be a highly effective strategy for managing long-term pain conditions. Research, including a comprehensive meta-analysis, shows that approximately 70-80% of patients experience meaningful improvements after completing physical therapy. These improvements include reductions in pain intensity—often by 40-50%—and significant gains in functional ability.
The therapies used are diverse and tailored to patient needs. Techniques such as hot packs, ultrasound, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), and therapeutic exercises target pain sources and promote healing. For example, individualized treatment plans combined with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) have been shown to increase success rates in pain relief by up to 84%.
Moreover, physical therapy addresses the underlying causes of pain, helping improve mobility and strength while reducing dependency on medications like opioids. It is especially effective for conditions like low back pain, osteoarthritis, and post-surgical rehabilitation, often reducing the need for invasive procedures by as much as 33%.
Patients attending therapy regularly tend to report higher satisfaction, with 88% stating they found physical therapy beneficial. The overall success rate, supported by extensive research, generally falls within 68-72%, with some studies citing even higher rates for specific conditions. These outcomes emphasize physical therapy’s vital role in long-term symptom management and functional recovery.
Physical therapy techniques for chronic pain
The intervention methods include manual therapies such as joint mobilization and myofascial release, along with modalities like ultrasound, heat therapy, and electrical stimulation. Structured exercise programs focus on strengthening, stretching, and restoring movement patterns.
Long-term pain relief and functional improvement
Evidence indicates that sustained improvement in pain and function can last up to one year post-treatment. Patients who complete more visits and have longer care episodes experience better outcomes, demonstrating the importance of consistent engagement in physical therapy.
Alternatives to opioid therapy
Physical therapy offers a significant alternative to opioid medications, which carry risks of dependency, overdose, and other health complications. Early intervention in primary care can lead to a 10% reduction in long-term opioid use, with therapy reducing the likelihood of opioid reliance by nearly half.
Integration with mindfulness and holistic approaches
Combining physical therapy with mindfulness practices and holistic approaches enhances stress management and overall well-being. Such multimodal strategies address both physical and psychological aspects of pain, leading to more comprehensive care.
| Technique | Purpose | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Manual therapy (joint mobilization, myofascial release) | Reduce muscle tension and restore movement | Pain relief, increased mobility |
| Modalities (ultrasound, heat, TENS) | Stimulate healing and decrease inflammation | Short-term pain reduction |
| Therapeutic exercises | Strengthening, flexibility, stability | Long-term functional improvements |
Physical therapy continues to evolve with data analytics, allowing practitioners to customize treatments based on patient progress. Its proven effectiveness, high satisfaction rates, and role in reducing opioid dependency underscore its importance in managing chronic pain.
Attendance, Completion Rates, and Their Impact on Outcomes
What are physical therapy attendance statistics?
In studies involving patients with chronic low back pain, the overall attendance rate to physical therapy sessions was approximately 73%. This high participation level shows that most patients engage actively in their treatment plans.
What factors influence self-discharge rates?
Interestingly, about 55% of patients with chronic pain self-discharged from physical therapy before completing their recommended course. Factors that affected these decisions included the number of visits attended and the length of the treatment episode. Patients who completed more visits and had a longer duration of care generally had a lower likelihood of self-discharging.
Additionally, the comfort level of therapists in treating chronic pain played a role. Therapists who rated themselves as more comfortable with managing chronic cases tended to have higher patient attendance and lower self-discharge rates.
How does session completion impact pain relief and function?
Patients who stay committed to their physical therapy sessions typically experience better outcomes. Studies show that increased attendance correlates with significant improvements, including reductions in pain scores such as Visual Analog Scale (VAS), and enhancements in functional measures like the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI).
In fact, patients who complete more therapy visits tend to report higher satisfaction and better long-term results, including sustained pain relief and improved mobility. This underscores the importance of consistent participation in therapy programs for optimal recovery.
In summary, maintaining high attendance and minimizing early discharges are crucial. They significantly influence the effectiveness of physical therapy in alleviating pain and restoring function, especially in chronic low back pain cases.
Physical Therapy’s Role in Opioid Reduction and Health Cost Savings
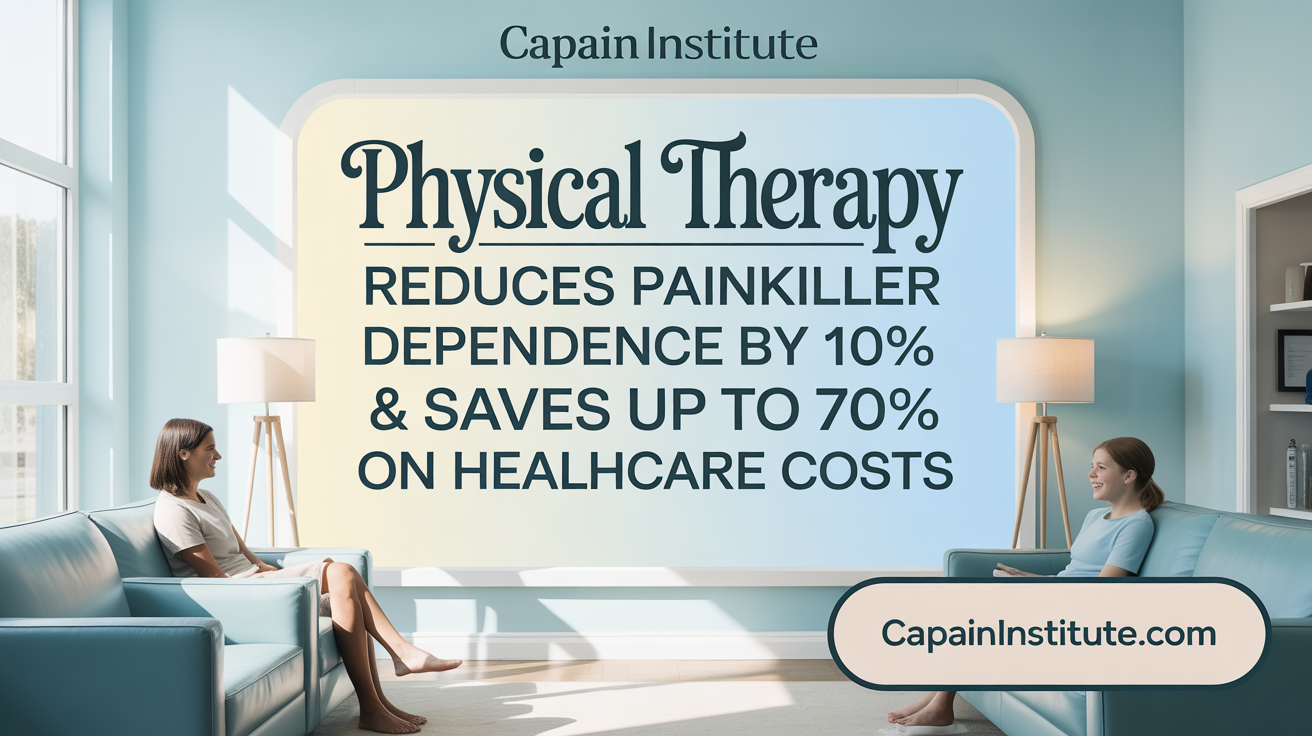
How does physical therapy contribute to reducing opioid use?
Physical therapy is a crucial component in managing chronic pain without relying heavily on opioids. Studies show that patients who see a physical therapist first for low back pain or other musculoskeletal conditions are less likely to start opioids early or develop long-term dependency. In fact, initiating physical therapy reduces the odds of opioid abuse by approximately 10%, according to recent research.
Physical therapy interventions, including therapeutic exercises, modalities like ultrasound, and TENS, effectively decrease pain and improve function. This approach not only offers pain relief but also minimizes the need for opioids, which carry risks of fractures, cardiovascular problems, and increased mortality.
What are the cost benefits of physical therapy compared to surgical treatments?
Compared to invasive procedures, physical therapy presents a more cost-effective option. Treatment costs can be significantly lower, with reductions reaching up to 70% when replacing surgery for certain conditions. Additionally, physical therapy can shorten recovery times by 20-30%, leading to faster return to daily activities and reduced lost productivity.
Patients who undergo physical therapy generally experience a 60% improvement in function after completing their course, which can also help prevent further health complications and hospital readmissions.
How does physical therapy influence long-term opioid dependency?
Implementing physical therapy as part of a comprehensive pain management plan encourages a shift away from long-term opioid use. Data indicate that early physical therapy not only improves pain and functional outcomes but also decreases the probability of patients becoming dependent on opioids over time.
This approach contributes to reducing healthcare costs and improves overall patient safety. High satisfaction rates—around 88%—highlight how patients value physical therapy' effectiveness as an alternative to medications.
| Aspect | Impact | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Opioid Use | 10% reduction in long-term dependency | Initiating PT early decreases probabilities |
| Cost Savings | Up to 70% compared to surgery | Shorter recovery and less invasive |
| Patient Satisfaction | 88% report satisfaction | High perceived effectiveness |
| Functional Improvement | 60% improvement post-treatment | Benefits in daily living |
Considering these factors, physical therapy emerges as a vital strategy to address pain sustainably while reducing dependence on opioids and lowering healthcare costs.
Industry Growth, Workforce, and Economic Impact of Physical Therapy

What are the current statistics of the physical therapy workforce?
The physical therapy industry employs approximately 259,200 professionals as of 2023. Many of these therapists hold at least one specialty certification, with orthopedic, sports, and neurologic specialties being the most common. The median annual salary for physical therapists was about $91,010 in 2020, and recent data from May 2024 indicates a rise, with median wages reaching approximately $101,020.
What are the growth projections and the number of job openings?
The profession is expected to experience substantial growth over the next decade. Employment of physical therapists is projected to grow by 14% from 2023 to 2033, adding roughly 13,600 new positions annually. Overall, about 259,200 jobs are held currently, with an anticipated 13,600 new job openings each year, reflecting a robust and expanding sector.
What is the economic impact of physical therapy?
The physical therapy industry significantly impacts healthcare costs and patient outcomes. It is estimated that physical therapy can reduce healthcare expenses by up to 70% compared to surgical interventions. Additionally, the high success rates—ranging from 68% to 72%—and high patient satisfaction, with 98% willing to recommend therapy, demonstrate its effectiveness and value. Furthermore, physical therapy's role in reducing opioid use by approximately 45% underscores its importance in safe pain management strategies.
| Aspect | Statistics | Additional Details |
|---|---|---|
| Workforce Size | 259,200 active therapists (2023) | Many hold specialty certifications |
| Projected Growth | 14% growth (2023-2033) | Adds about 13,600 jobs annually |
| Median Salary (2024) | $101,020 | Up from $91,010 in 2020 |
| Industry Impact | Up to 70% healthcare cost reduction | High success and satisfaction rates |
| Certification and Skills | 42% with advanced certifications | Specializations include orthopedic, sports, neurology |
This evidence shows that the physical therapy industry is not only vital for patient health but also a growing economic sector with promising career prospects.
Innovations and Emerging Trends in Physical Therapy Effectiveness

What are the current trends and patterns in physical therapy effectiveness for pain relief?
Recent developments in physical therapy focus on delivering more personalized and data-driven care. The use of high-tech tools such as wearable sensors enables therapists to monitor patient movements in real-time, tailoring exercises to individual needs and improving treatment precision.
Data analytics plays a significant role in evaluating treatment outcomes. Systems like the Rehab Outcomes Management System (ROMS), used at BU's Physical Therapy Center, collect standardized patient data, allowing clinicians to analyze treatment success rates, predict outcomes, and refine interventions. For example, success rates for conditions like rotator cuff tendonitis increase as patients complete more visits, highlighting the importance of tailored, ongoing care.
Telehealth has become a vital component, expanding access, especially for patients in remote areas or with mobility issues. Virtual consultations and remote therapy sessions allow continuous monitoring and adjustments, maintaining high satisfaction and effectiveness. Studies indicate that early intervention via telehealth can significantly improve recovery outcomes.
Innovative treatment modalities are also emerging, including robotic-assisted therapy, aquatic therapy, and regenerative medicine techniques. These approaches enhance traditional physical therapy by promoting faster recovery and better pain relief.
The integration of multidisciplinary strategies—combining physical therapy with mental health support, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and holistic health models—addresses the complex nature of chronic pain comprehensively. This approach has demonstrated increased success rates, with individualized treatment plans improving pain relief from around 38% to over 80%.
In summary, current patterns in physical therapy emphasize technological advancements, remote care, and holistic, patient-centered approaches. These innovations are transforming pain management by making treatments more effective, accessible, and personalized, promising better outcomes for diverse patient populations.
Multimodal and Individualized Physical Therapy Approaches
What are the benefits of combining physical therapy with cognitive behavioral therapy?
Integrating cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) with physical therapy significantly enhances treatment outcomes for chronic pain patients. A meta-analysis by Goethe University Frankfurt found that when combined, this multimodal approach elevated pain relief success rates by 84% compared to standard treatment alone. This synergy addresses both the physical and psychological factors of chronic pain, leading to more sustained relief and improved quality of life.
How effective are individualized treatment plans?
Personalized treatment strategies have been proven to be more effective than generic ones. The same meta-analysis highlighted that customized therapy increased the success rate for pain relief by 38% over standard methods. Tailoring interventions to specific patient needs—such as activity levels, conditions, and psychological state—can improve overall effectiveness and foster greater patient engagement.
What are the long-term outcomes associated with multimodal therapy?
Evidence suggests that combining physical therapy, exercise, and medical treatment produces substantial long-term benefits. Patients benefit from sustained pain relief and functional improvements for up to a year post-treatment. For instance, studies show that approximately 70% report meaningful improvements in function and quality of life after completing these comprehensive programs. Furthermore, early intervention and personalized therapy can reduce reliance on opioids and decrease recovery time by 20-30%.
| Aspect | Effect | Additional Details |
|---|---|---|
| Success Rate | Up to 80-90% for acute cases | Includes conditions like acute lower back pain and post-surgical rehab |
| Long-Term Effectiveness | Sustained improvements up to a year | Enhances quality of life and functional capacity |
| Integration with CBT | Increases success by 84% | Addresses both physiological and psychological factors |
| Customized Treatment | Improves success by 38% | Tailors interventions to individual patient profiles |
| Patient Satisfaction | About 88% highly satisfied | Reflects positive patient perceptions and perceived effectiveness |
These insights underscore the advantages of adopting a comprehensive, patient-centered approach in physical therapy to optimize outcomes and improve long-term health.
Physical Therapy Outcomes in Specific Conditions: Case Examples
How effective is physical therapy for chronic low back pain?
Studies show that physical therapy significantly alleviates pain and improves functional status in patients with long-term low back pain. In a comprehensive meta-analysis involving over 10,000 patients, individualized therapies combined with cognitive behavioral therapy increased success rates in pain relief by 84% compared to standard treatments. Patients often experience a reduction in Visual Analog Scale (VAS) scores by 40-50%, with about 70% reporting meaningful improvements in function and quality of life.
What are the results of physical therapy in post-surgical orthopedic cases?
Physical therapy plays a crucial role after surgeries such as hip arthroplasty. Preoperative and postoperative physiotherapy can reduce pain, shorten hospital stays, and enhance functional recovery. For instance, targeted preoperative physical therapy has demonstrated significant reductions in pain levels and better postoperative outcomes. Overall, PT interventions contribute to a 20-30% faster recovery timeline and can help reduce the need for additional surgeries by approximately one-third.
How does physical therapy impact neurological conditions and osteoarthritis?
Patients with neurological disorders and osteoarthritis often show notable benefits from physical therapy. Exercise therapy helps improve mobility, decrease pain, and restore function. For example, treatments for hip and knee osteoarthritis can lead to a 50% decrease in pain intensity within about 4-6 weeks. Additionally, individuals with complex regional pain syndrome and neurological impairments have experienced substantial functional improvements, with success rates ranging between 60-80%.
What success rates are seen in cardiopulmonary rehabilitation programs?
Cardiopulmonary rehab offers remarkable results, with up to 80% of patients achieving significant improvements in exercise capacity and overall health. These programs have a high engagement rate, and patients often report increased quality of life and physical endurance. The structured approach, focusing on exercise and lifestyle modifications, is highly effective in managing chronic respiratory and cardiac conditions.
The overall evidence underscores that tailored, multimodal physical therapy approaches generally deliver success rates ranging from 68% to 84% in various conditions, markedly improving pain, mobility, and quality of life for diverse patient groups.
Key Takeaways on Physical Therapy Success Rates for Pain Relief
The extensive body of scientific research and clinical data underscores that physical therapy is an effective and patient-valued intervention for pain relief and functional improvement across a variety of conditions. Success rates ranging between 68% and 72%, combined with high patient satisfaction, demonstrate its reliability as a frontline treatment. Physical therapy’s advantages include reducing opioid dependency, lowering surgery rates, enabling quicker recovery, and offering cost-effective care. The evolving landscape features personalized, technology-enhanced, and integrative approaches that promise to further enhance outcomes. As the physical therapy profession continues to grow and adapt, it remains a critical component in modern pain management strategies, aligning clinical effectiveness with patient-centric care and systemic health benefits.
References
- Effectiveness of physical therapy and exercise on pain and ...
- Factors Associated With Physical Therapy Attendance Rate and Self ...
- Physical Therapy Statistics - April ABA
- Treatment for back pain: 84 percent increase in success rate
- Physical Therapy Statistics: How Effective Is PT and What Do the ...
- Better Treatment through Big Data - Boston University
- [PDF] How Physical Therapy Transforms Pain Management To Improve ...
